Digital Dentistry: Innovative Solutions for Your Teeth
The development in dentistry is progressing steadily. In this article, we would like to introduce both the revolutionary and already proven CAD/CAM procedure as well as the latest developments in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
CAD/CAM procedure with 3D scan
The CAD/CAM procedure has revolutionized dentistry. CAD (Computer Aided Design) allows for the precise design of dental restorations on the computer, while CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) enables the direct production of dental restorations from high-quality materials.
The benefits of this technology include the reduction of errors and the acceleration of the manufacturing process. Patients benefit from customized dental restorations that can often be completed in just one session.
The entire process is made more comfortable and precise, as the traditional impression process is no longer necessary. Whether crowns, inlays, bridges, or implants, modern dental practices work with CAD/CAM systems. High-quality materials ensure aesthetic and durable results. Thus, CAD/CAM combines precision with efficiency as an innovative solution for high-quality dental restorations.
Functioning and Production
The production of dental restorations using Computer Aided Design (CAD) and Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) essentially takes place in four steps. These can be divided as follows:
3D scan of CAD/CAM dental restorations
Instead of a traditional impression with impression material, a 3D scan is taken. Using an intraoral scanner, the structure of the tooth and surrounding tissue is precisely captured. This procedure is not only more comfortable for the patient but also provides highly accurate digital models. The data obtained helps to design and fabricate the dental restoration. Digital impressions avoid distortions or inaccuracies that can occur with traditional impression methods, ensuring an optimal fit.
The computer-assisted design of the dental restoration:
Using specialized CAD software, the dental restoration is designed after the digital impression. The dental technician precisely models the crown, bridge, or inlay on the screen, taking factors such as bite height, tooth color, and fit into account. Before the restoration is made, adjustments can be made in real-time through computer simulation. The CAD process allows for extremely high precision and customization of the dental restoration.
Milling of the CAD/CAM dental restoration:
Once the digital design is completed, the dental restoration is milled from a block of ceramic or another material using computer-controlled milling machines. This CAM process ensures that the shape of the restoration exactly matches the calculated data. The precise milling achieves a perfect fit and high stability. To further optimize the aesthetics and surface, manual finishing is carried out by the dental technician after milling.
Insertion of the dental restoration:
After the production, the dental restoration is placed by a dentist. Everything is customized to the individual needs of the patient.
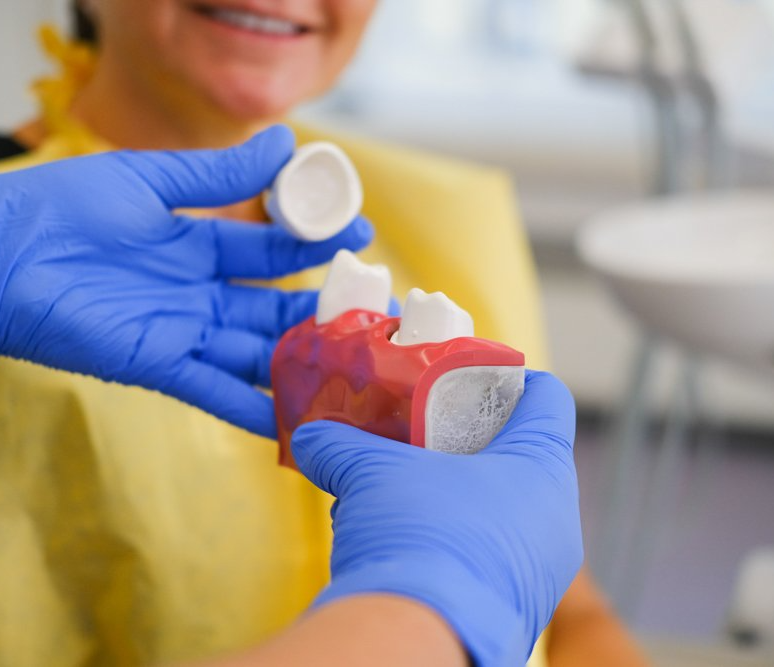
Materials Used in the CAD/CAM Process
The dental prosthesis can be made from various high-quality materials in the CAD/CAM process. Ceramic is one of the most commonly used materials due to its similarity to natural tooth color and high biocompatibility.
Zirconia is one of the most durable variants, known for its high strength and aesthetics, and is particularly suitable for crowns and bridges. Hybrid ceramics are characterized by high elasticity and are primarily used for inlays or partial crowns. Composites are also used for minimally invasive restorations due to their properties.
Thanks to modern manufacturing techniques, all materials can be processed precisely. The result is a durable and well-fitting dental prosthesis. Ultimately, the aesthetic, functional, and individual needs of the patient determine the choice of the appropriate material.
Artificial Intelligence in Dental Technology
Dentistry and dental technology are undergoing a profound transformation, largely due to Artificial Intelligence (AI). The production of dental prosthetics, the diagnosis of diseases, and the planning of treatments were previously heavily reliant on human expertise and manual labor.
Modern AI systems enable significant automation and precision enhancement. AI opens up new possibilities to increase efficiency and optimize patient care.
This development will progress even faster in the coming years. Below, we present some examples of AI applications in dental technology. Both patients and dental professionals benefit from these new technologies.
AI in Diagnostics: More Accurate Early Detection of Dental Diseases
One of the key advancements enabled by AI is its improvement of dental diagnostics. Dental diseases such as cavities, periodontitis, or even early signs of oral cancer can be detected more quickly and accurately through the use of deep learning algorithms.
AI-supported image analysis programs can evaluate X-rays, intraoral scans, and 3D images in seconds. They detect minute discrepancies that are often difficult for a dentist to see with the naked eye.
AI offers significant advantages, especially in the early detection of cavities or inflammatory processes. It highlights suspicious areas and provides a risk assessment, which serves as a decision-making aid for the dentist.
Personalized treatment planning through AI.
To develop customized treatment plans, algorithms can analyze various factors such as the individual
bite situation, bone density, or the course of the disease.
Orthodontics
In orthodontics, AI can precisely analyze tooth movements and design detailed schedules for aligner therapy.
This not only shortens the treatment duration but also enables the early detection of unexpected complications.
Implantology
In implantology, AI can enable the optimal positioning of dental implants based on CT or MRI scans.
This reduces risks and helps plan the surgical procedure more effectively.
Improved Patient Communication
In addition to providing technical support for dentists and dental technicians, AI also improves communication with patients. Frequently asked questions, appointment reminders, or explanations of treatment procedures can be answered by virtual assistants in an understandable language.
Practices can even use AI to reduce patients' fear of visiting the dentist. For example, augmented reality apps or AI-supported simulations allow patients to see what the procedure will look like. This helps build trust and increases overall satisfaction.
Future Perspectives
The development of artificial intelligence can be divided into three phases: ANI, AGI, and ASI. We are still at the beginning of this development.
Artificial Narrow Intelligence
ANI (Artificial Narrow Intelligence) is the phase we are currently in. These systems are programmed to perform specific tasks. They do not yet have a deeper understanding of relationships in dentistry or dental technology.
This category includes voice assistants, image recognition systems, or recommendation systems. While they can deliver impressive performance within their domain, they lack the ability to think independently or solve problems outside of their defined application area.
Artificial General Intelligence
AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) is the next stage of development. These systems would be capable of flexible thinking, independently handling various tasks, and drawing logical conclusions – similar to a dentist.
AGI would be able to learn autonomously, develop creative solutions, and adapt to new challenges. Despite intensive research, a true AGI does not yet exist. However, experts anticipate that it could be developed in the coming decades.
Artificial Super Intelligence
ASI (Artificial Super Intelligence) represents the final stage. It would surpass humans in all cognitive abilities and be capable of independently generating knowledge. Such systems would have the potential to accelerate major scientific breakthroughs, but they also pose risks.
Whether and when the next stages will be reached remains uncertain. However, it is clear that AI will play a crucial role in shaping the future of dentistry and the dental practice of tomorrow.